Cole3D heeft een informatief artikel geschreven over transistors, die kleine dingetjes die in elke chip zitten en de basis van de hedendaagse computer vormen. Voor iedereen die nog niet weet hoe en wat transistors zijn verplichte literatuur dus ![]() :
:
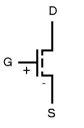
In its simpliest form a transistor is a semiconductor device with three leads or connections. A very small current or voltage (depending on which transistor is being used) at one connection can control a much larger current flowing through the other two leads. This means that the transistor has two uses, an amplifier or a switch. Now if you remember, all digital devices including processors only "think" in two different states -- on and off, which are represented by a 1 and 0 respectively. Because of this, we will be only focusing on the switching capabilities of the transistor.There are two main families of transistors, bipolar and field effect. We will be looking at the field effect transistor (better known as a FET) and more specifically the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor, whoa that's a big one). Below is a circuit diagram of an everyday MOSFET:
Here you can see there are three terminals on the device, the Drain, Source and Gate. In this device the drain and source are connected, so electrical current will flow from the drain to the source. The gate on the other hand is not connected directly to the drain or the source. Instead it is separated by a layer of silicon dioxide. All MOSFETs are N-type or P-type.