Introduction
 AMD's Opteron has remained loyal to Socket 940 since its introduction in April 2003, but all good things must come to an end some time. A new series of processors will soon appear which will work with a new socket, dubbed Socket F. There are a number of different reasons behind this transition, and some of them will only become clear in the future. For the user, the most tangible difference is the support for DDR2 memory. Even though DDR2 offers up to double the bandwidth of regular DDR, tests regarding desktop usage have shown that the increase in performance is small or even negative. In this article, we will take a look at the effect of this new memory type in our database test.
AMD's Opteron has remained loyal to Socket 940 since its introduction in April 2003, but all good things must come to an end some time. A new series of processors will soon appear which will work with a new socket, dubbed Socket F. There are a number of different reasons behind this transition, and some of them will only become clear in the future. For the user, the most tangible difference is the support for DDR2 memory. Even though DDR2 offers up to double the bandwidth of regular DDR, tests regarding desktop usage have shown that the increase in performance is small or even negative. In this article, we will take a look at the effect of this new memory type in our database test.
 Socket F
Socket F
Socket F is no traditional socket but a so-called Land Grid Array (LGA). This means that there are no pins on the processor, but only small pits. These make contact with the slightly springy landing-points on the mainboard. This approach gives multiple advantages, such as a higher contact point density and better electrical properties. In total, Socket F has 1207 lands, but their individual functions have not been fully unraveled yet. Rumors trying to explain the extra positions include that there is space for an integrated PCI Express controller and a fourth HyperTransport link. Furthermore, support for FB-DIMM is supposed to be possible. Socket F should also be prepared for the electric current demand of quad cores.
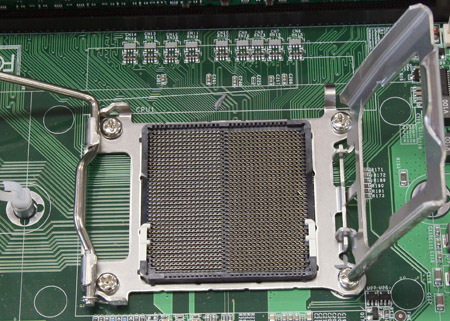
Looking at the photo of the socket, it is obvious the mechanism to mount the cooler has changed. AMD has designed a metal construction including a cover to make sure that the cooler can be attached firmly without running the risk of damaging the processor and, more importantly, the underlying lands. These lands are clearly divided in two halves, yet the reason for this is unknown to us. AMD did announce that it wants to work with different power planes, allowing specific parts of the processor to get an independant supply, but a physical division of lands is unnecessary for that purpose. The two lands are not completely the same: the right land (on this picture) has 18 rows of pins, the left one has only 17 rows.
The Socket F Opteron will be recognizable by the new model numbering with four digits. Also Socket F chips will be at least dual core, so single core processors won't be found in the assortment. According to rumor, the new numbering scheme will look like this:
| Clock speed | 1-way | 2-way | 4/8-way |
|---|
| 1,8GHz | 1210 | 2210 | 8210 |
| 2,0GHz | 1212 | 2212 | 8212 |
| 2,2GHz | 1214 | 2214 | 8214 |
| 2,4GHz | 1216 | 2216 | 8216 |
| 2,6GHz | 1218 | 2218 | 8218 |
| 2,8GHz | 1220 | 2220 | 8220 |
The system
We can't really speak of a test system. Initially, we only had the disposal of a sample of a MSI Socket F mainboard, the K9SD Master-A8R. In a roundabout way, we managed to lay our hands on two 2,4GHz Opteron 2216 processors. Using these components, we knocked together a test set-up. Due to the absence of suitable coolers for Socket F processors, we had to improvise considerably with some tie wraps to keep a pair of alternative coolers in their place. Furthermore, the lack of a casing resulted in an air flow deficiency, which was solved by placing an air conditioner right next to the set-up.




The memory also presented a problem. Everything worked smoothly with 4GB DDR2-667, but we preferred to use 8GB for the benchmarks since we tested the Sun Fire X4200 (the dual Socket 940 machine from the previous review) with 8GB as well. Unfortunately, we were unable to create a stable configuration with the DDR2-553 memory taken from a Sun T2000 system in the Socket F mainboard. It is of course too early to wag a finger at anyone, since we're not dealing with final hardware. Nevertheless it's important to keep this in mind while viewing and interpreting the results. The few tests that did come through with 8GB memory show no large difference compared to 4GB, but it is present anyway:

MySQL 4.1, 5.0 and 5.1
Three different versions of MySQL have been tested, namely 4.1.20, 5.0.18 and 5.1.9 (beta). In our tests, the differences between those turned out to be minimal: for all three versions, the new Opteron with DDR2-667 proved to be slower than the current model with DDR400. On average, over all versions, load levels and number of cores, Socket F loses to Socket 940 with a difference in performance of approximately 8 percent. Even if we increase the results of Socket F slightly to compensate for the fact that the Socket 940 system had more memory on board, the net loss remains. The extra 4GB of memory only delivered an increased performance of about 2 percent in our situation.
With faster memory (DDR2-800), the performance of the new Opteron could possibly be bumped up slightly. However, it is clear that the effect of Socket F's extra memory bandwidth in certain cases (such as our web site database) can be minimal. This conclusion is no big surprise, since we observed the same pattern for Socket AM2 in desktop systems. Still, there are conceivably situations where the DDR2 memory does give a boost in performance.



PostgreSQL 8.2
In our previous review we presented test results that were gathered with PostgreSQL as a database for the first time. Since its performance and scalability positively suprised us, we'll definately keep using it in future reviews. Like before, it didn't turn us down this time. While the performance of MySQL clearly went downhill after the switch to DDR2, PostgreSQL was able to hold on to it. On average, only 1 percent of its performance was lost after the transition. This would even mean a small victory for the DDR2 Opteron if the same amount of memory had been used.

When we compare the performance of MySQL and PostgreSQL on the platform of two dual core Socket F processors, an apparent pattern emerges regarding the strengths and weaknesses of the two packages. MySQL outperforms PostgreSQL when under a load of up to ten simultaneous users. Above that number, the curve bends and performance starts to decrease again. In contrast, PostgreSQL holds on comfortably to its performance peak, even at a concurrency of 100.

Conclusion
Even though Socket F appears to have a lot of potential in store, the first Opterons that hook into it don't really seem to profit from that. The most positive conclusion we can draw is that the performance is roughly equal to that of Socket 940. Nevertheless, the migration to DDR2 memory does come with a number of advantages. DDR2 is becoming cheaper than its predecessor and consumes less power. However, the availability of registered DDR2 for servers is not as good as that of its normal desktop variant. In our pricewatch, at this moment only registered DDR2-400 is well available, having a price similar to registered DDR400 memory. The DDR2-533 and DDR2-667 versions of the server memory are rarer and more expensive, and are furthermore troubled with comparatively high latencies. Registered DDR2-800 is nowhere to be found in our price database.

:fill(black)/i/1154193581.jpg?f=thumb)
:fill(black)/i/1154193714.jpg?f=thumb)
:fill(black)/i/1154193715.jpg?f=thumb)
Socket F does make a good investment for the future. For instance, it probably won't be a problem to put a quad core K8L into this socket, which is expected to arrive half way next year. Whoever is in the market for an Opteron server therefore does the right thing when choosing for Socket F instead of Socket 940, even though there is no direct performance advantage. AMD's new socket will nevertheless not be able to do much about the advance of the Intel Woodcrest. Keep an eye on Tweakers.net to find out how Intel's latest Xeon performs in this test.
 Words of thanks
Words of thanks
 Tweakers.net would like to thank MSI for lending us the Socket F mainboard, A-Data for sponsoring the DDR2 server memory, Inge Janse for the English translation and of course ACM and moto-moi for their valiant efforts of building the system and executing the benchmarks.
Tweakers.net would like to thank MSI for lending us the Socket F mainboard, A-Data for sponsoring the DDR2 server memory, Inge Janse for the English translation and of course ACM and moto-moi for their valiant efforts of building the system and executing the benchmarks.
 Previous articles in this series:
Previous articles in this series:
 27-7-2006: Sun UltraSparc T1 vs. AMD Opteron (Dutch)
27-7-2006: Sun UltraSparc T1 vs. AMD Opteron (Dutch)
 19-4-2006: Xeon vs. Opteron, single- en dualcore (Dutch)
19-4-2006: Xeon vs. Opteron, single- en dualcore (Dutch)
 AMD's Opteron has remained loyal to Socket 940 since its introduction in April 2003, but all good things must come to an end some time. A new series of processors will soon appear which will work with a new socket, dubbed Socket F. There are a number of different reasons behind this transition, and some of them will only become clear in the future. For the user, the most tangible difference is the support for DDR2 memory. Even though DDR2 offers up to double the bandwidth of regular DDR, tests regarding desktop usage have shown that the increase in performance is small or even negative. In this article, we will take a look at the effect of this new memory type in our database test.
AMD's Opteron has remained loyal to Socket 940 since its introduction in April 2003, but all good things must come to an end some time. A new series of processors will soon appear which will work with a new socket, dubbed Socket F. There are a number of different reasons behind this transition, and some of them will only become clear in the future. For the user, the most tangible difference is the support for DDR2 memory. Even though DDR2 offers up to double the bandwidth of regular DDR, tests regarding desktop usage have shown that the increase in performance is small or even negative. In this article, we will take a look at the effect of this new memory type in our database test.![]() Socket F
Socket F












:fill(black)/i/1154193581.jpg?f=thumb)
:fill(black)/i/1154193714.jpg?f=thumb)
:fill(black)/i/1154193715.jpg?f=thumb)
 Tweakers.net would like to thank
Tweakers.net would like to thank